Basic Web Hosting, easy to understand
Basic knowledge about Web Hosting, suitable for those who are starting to study website technology, types of Hosting, working formats, server working, basic terminology about Web Hosting, suitable for beginners who want to start creating a website but are still confused with the words Hosting, Domain, VPS, or Cloud. Here we will compare to give a clear picture.
🌐 What is Web Hosting?
Web Hosting is A service that provides space on the Internet to store your website.
Simply put, it is like:
- 💻 website = home
- 🗂️ Web files Such as images, web pages, code = furniture
- 🏠 Web Hosting = Land or space for placing a house online
If there is no Hosting → Your website will have no place for people to visit.
🛠️ So what does Hosting do for us?
- ✅ Save website files
- ✅ Make your website online and accessible through your browser
- ✅ Connect to a domain name (website name)
- ✅ There are management systems such as database, email, security, etc.
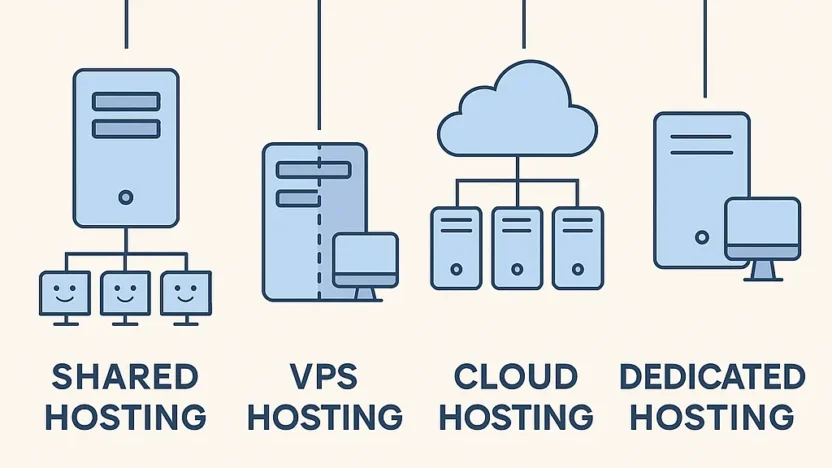
📦 How many types of web hosting are there? What are they❓
🧐 There are many types of Web Hosting such as:
| Hosting Type | Who is it suitable for? |
|---|---|
| Shared Hosting | Small website, small budget, beginners starting out |
| VPS Hosting | Growing websites need more control |
| Cloud Hosting | A website that emphasizes stability and supports a large number of people. |
| Dedicated Hosting | Very large website with a lot of traffic. |
| Email Hosting | Email Business or organization |
Shared Hosting = Hosting at You share server space with multiple other websites.
🛏️ It's like "living in a dorm" or "living in a flat where you share a kitchen and bathroom."
That is, you are not alone. There are multiple websites shared on the same device.
- Very cheap price 💸
You can start a website with just $1-$30 per month. - Easy to use
Often comes with a management system (e.g. cPanel) that lets you click and install WordPress without any technical knowledge. - Suitable for beginners
Anyone who is just starting out with a website, such as a personal blog, profile website, or small business referral website → Yes, that's right!
- Share resources with others
If other websites on the same server “use a lot of resources”, your website may become slow or crash 😅 - Limited control
You can't install any special software or customize the server too much. - Not suitable for large websites/many visitors
For example, a sales website with a lot of customers visiting it or a website that downloads a lot of images/videos.
🎯 Summary | Who is it suitable for? | ✅ Newbies to website creation, small websites, low budget | | Not suitable for? | ❌ Websites with a lot of visitors, the website must be very fast/stable |
2. 🖥️ What is VPS Hosting?
VPS Abbreviated from Virtual Private Server Or directly translated as “virtual private server”
- 📦 VPS Hosting = Dividing a large server into multiple “sub-servers”.
- Each person will get their own private space, no need to share with others like with Shared Hosting.
🏠 Compare and visualize:
- Shared Hosting = Living in a shared room, sharing everything with other people.
- VPS Hosting = Living in my own condo, with a private room, separate electricity, water, and internet systems.
- Dedicated Hosting = I rent the whole building and live alone. 😄
✅ Advantages of VPS Hosting:
- Personal resources 🧠
The CPU, RAM, and Storage you get = are yours alone, no need to share with anyone. - More stable and faster than Shared Hosting
Suitable for websites with a lot of visitors or serious businesses. - More control
You can install the software yourself, restart the server yourself, and customize the system as you wish. - Easy to expand resources
If the website grows, you can immediately add CPU/RAM/Storage without having to move the server.
⚠️ Things you should know:
- ❌ Some server knowledge is required.
Especially if it is an unmanaged VPS (must manage everything yourself, such as installing the system, setting up security) - 💰 More expensive than Shared Hosting
But it is still cheaper than renting an entire server (Dedicated Hosting).
🎯 Simple summary | Who is it suitable for? | ✅ Medium-large websites, businesses, sales websites, people who want to control the system themselves | | Who is it not suitable for? | ❌ Newbies who don't want to get involved with technical matters or small websites with a small budget |
3. ☁️ What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud Hosting It is a hosting service that uses Multiple servers connected together as a group (Cloud) To make the website fast, stable and support a large number of users.
- 💡 If Shared Hosting = stay in a dorm
- VPS = Condo
- Cloud Hosting = Live in a smart home with a complete backup system for power, water, and internet! 🏡⚡
✅ Advantages of Cloud Hosting:
- Very stable 🔒
If one server goes down, your website still works because the system immediately distributes the load to the other servers. - Scalable 🚀
If the website has more visitors → Increase CPU, RAM, Storage immediately in real-time. - So fast!!! ⚡
Because it uses multiple devices to help process + intelligent traffic management - Safer
Cloud systems often have good firewalls, backups, and DDoS protection. - Pay as you go (Some) 💸
For example, if you use a little, pay a little. If you use a lot, pay more. You don't have to pay a lump sum like with Shared/VPS.
⚠️ Things to know before using Cloud Hosting:
- 💰 Higher price Shared Hosting but “worth it” if your website is important
- 🛠 Some services may require some technical knowledge (but some have a team to manage it).
| 🎯 Who is it suitable for? Who should use Cloud Hosting? |
|---|
| ✅ Business website / e-commerce / website that must not crash |
| ✅ Websites with a lot of visitors or fast growth |
| ✅ People who want high speed, stability and security. |
| ✅ Web applications such as booking systems, ordering systems, etc. |
4. 🖥️ What is Dedicated Hosting?
Dedicated Hosting It is a rental. 1 full server To be used solely for your website.
💡 Simple comparison:
- Shared Hosting = Dormitory, sharing a room with other people
- VPS = Condo with private space but still in the same building.
- Dedicated Hosting = Single house! 🏠 The whole house is yours, no one will share it.
✅ Advantages of Dedicated Hosting:
- Maximum efficiency 💪
CPU, RAM, Storage all = yours alone - The website is very powerful and stable. ⚡
Because no one is competing to use the resources. - Absolutely safe 🔒
No other websites will share your device with you, reducing security risks. - 100% system control
You can install anything you want, customize the server in any way you want (Root Access) - Suitable for very large websites such as
- Websites with a large number of concurrent users
- Online games
- Real-time booking/trading system
⚠️ Dedicated Hosting Limitations:
- 💸 expensive!
Starting at thousands to tens of thousands of baht/month because you rent the entire machine. - 🧠 Must have technical knowledge
If it is not a managed server, you have to take care of the server yourself, such as installing the OS, adjusting the firewall, and managing security.
🎯 Who is it suitable for?
| Suitable for… | Not suitable for… |
|---|---|
| ✅ Very large website, website with many visitors | ❌ Small websites, startup websites or test websites |
| ✅ Large companies, corporate back-end systems | ❌ People who don't want to manage the server themselves |
| ✅ Websites that require very high security | ❌ Limited budget |
5. 📧 What is Email Hosting ❓
Email Hosting It is a service that provides a space and system for managing email for businesses or individuals, where users can use their own domains (such as yourname@yourcompany.com) to send and receive emails, without having to rely on a common free email service (such as Gmail or Yahoo).
When you use Email Hosting You will get these:
- Email storage: You will have space to store sent and outgoing emails, such as inbox, sent items, drafts, etc.
- Private email domains: You can use your own domain name (e.g. @yourcompany.com) instead of using a free email service with a provider's domain name (e.g. @gmail.com).
- Security and additional features: Email hosting services often include features that help secure email use, such as anti-spam protection, data encryption, and the ability to connect to applications such as Microsoft Outlook or mobile email apps.
Examples of services Email Hosting namely:
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): A service from Google that lets you use Gmail with your own domain.
- Microsoft 365: A service from Microsoft that lets you use Outlook with your own domain.
- Zoho Mail: Email service suitable for small businesses
Why use Email Hosting?
- If you're a business or organization, using a professional-looking email domain (like info@yourcompany.com) can help build credibility for your business.
- It helps to make email management more systematic and has features that support enterprise-grade usage such as calendar sharing, archiving, and accessing email data from multiple devices.
In summary, Email Hosting It is a service that allows you to use a professional and secure email system using your own domain instead of the domain name of a common email provider.
| section | Shared Hosting 💻 | Cloud Hosting ☁️ |
|---|---|---|
| System Structure | Share the same server with multiple websites | Use multiple server networks (Cloud) |
| Stability | If other websites have problems, it may affect your website. | More stable because the system has multiple backup machines. |
| speed | Sharing resources with others | Dedicated and scalable resources |
| safety | Risk from other websites on the same device | It is safer because resources are separated. |
| Scalability | Very limited, if the site grows too fast you may have to move. | Easy to expand, add CPU/RAM as needed |
| price | 💰 Cheaper, starting at tens to hundreds/month | 💰 Higher but worth the stability |
| Who is it suitable for? | Newbie, small website, small budget | Websites that require speed, stability or fast growth |
- Shared Hosting It's like living in a dorm, sharing a kitchen and bathroom with others → Cheap, but limited in privacy, speed, and security.
- Cloud Hosting It's like living in a nice condo with backup power, water and Wi-Fi → The price may be higher, but it's stable and scalable.
🗂️ What is a database?
Database (Database) is Organized storage On the computer
Used to store, manage and retrieve various data that websites or apps require.
💡 Think simply:
- Database = filing cabinet
- each File = Data Table
- each Paper in file = Record row
- And you can quickly find/edit/delete these data 🚀
🧠 Give a clear example:
If it is an online store website:
| Tables in the database | Stored information |
|---|---|
users | Customer information such as name, email, password |
products | Product details such as name, price, inventory |
orders | Customer order information |
➡️ When we press "Order" on the website = the system will immediately save the information to the database.
SSD and NVMe SSD Easy to understand
What is SSD (Solid State Drive)?
SSD is Storage devices Used Semiconductor chip To store data instead of the old rotating hard disk drive (HDD)
📦 Easy comparison:
- HDD = rotating platter (like a record player)
- SSD = Digital storage (no moving parts)
Advantages of SSD:
- Several times faster than HDD 🚀
Because there are no rotating parts - More durable 💪
No moving parts, low risk of damage - Silence 🔇
No rotation of the plate - Consumes less power ⚡
More energy efficient than HDD
What is NVMe SSD?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is The technology used to communicate data between SSD and computer. This makes NVMe SSDs much faster than traditional SSDs. HOURS or SAS port
📦 Compare:
- SSD SATA = Just like driving on a normal road
- SSD NVMe = Like driving on a faster expressway 🚗💨Compare:
Advantages of NVMe SSDs:
- Maximum speed 🚀
Read/write data several times faster (can reach 3500 MB/s or more) - Reduce latency ⏱️
Ideal for high-speed applications such as working with large files, playing games, or doing graphics work. - Improved performance for multi-app usage
Improved support for reading/writing multiple data simultaneously
🔧 The difference between SSD and NVMe SSD:
| Point of comparison | SSD (SATA) | NVMe SSD |
|---|---|---|
| speed | Slow (about 500 MB/s) | Very fast (can reach 3500 MB/s or more) |
| Connection | Connect via SATA port | Connects via PCIe (several times faster than SATA) |
| price | Cheaper | More expensive (but provides good speed) |
| Usage | Suitable for general use | Suitable for tasks that require high speed (e.g. video editing, high-end gaming) |
💡 summarize:
- SSD (SATA) Suitable for general use, such as starting up your computer faster, storing files, or operating systems.
- NVMe SSD Suitable for applications that require maximum speed, such as gaming, graphics work, or processing large amounts of data.
What is the difference between Data Transfer and Bandwidth? ❓
📦 What is Data Transfer?
is The amount of data sent or received through the server in a given period of time.
For example, someone visits your website and loads images, loads web pages, videos, etc. These are all uses of Data Transfer.
- Units: Usually measured in GB or TB per month
- It's similar to a mobile phone package that says "50GB of internet per month".
💡 The more people visit the website or Large web content (e.g. lots of images/videos) The more you use Data Transfer
🚀 What is Bandwidth?
is Maximum data transmission speed Between server and user
Measures how fast a website can deliver data at any given time.
- Units: Usually measured in Mbps (Megabits per second) or Gbps
- Similar to home internet speed, such as “speed 100 Mbps”
💡 Bandwidth = Capacity of the “data transmission pipe”
Data Transfer = The amount of water that flows through that pipe in 1 month.
🌐 What is a CDN?
CDN Abbreviated from Content Delivery Network
is Network of servers Spread across the world to help Deliver data from websites faster Especially for users who are far from the main server.
💡 Give a visual example:
Let’s say your website is on a server located in “Singapore”.
But there are people from "France" who come to use it.
if No CDN:
France has to load the web from a server that is very far away → The web is slow and takes a long time to load 🐢
if Have CDN:
CDN will send data from “server closest to France” → Fast web! 🚀
🧩 How does CDN work?
- 📦 Keep a copy of your website files Such as images, CSS, JS, videos, etc.
- 🌍 Distribute these files to servers around the world. (called edge servers)
- 👤 When someone visits the website → CDN delivers the file from the point closest to the user.
→ Reduce web loading time = faster web!
✅ Advantages of using CDN:
| strength | explain |
|---|---|
| ⚡ Increase speed | Send files from a server near the user |
| 🛡️ Increased safety | Helps protect against DDoS |
| 🌍 Supports users worldwide | Suitable for websites with visitors from many countries. |
| 💾 Reduce the load on the main server | CDN helps to carry large files instead of the main server. |
| 🔁 Data Cache | Reduce repetitive data loading |
📌 Examples of popular CDN providers:
- Cloudflare 🌩️ (Free and very easy to use)
- Amazon CloudFront (AWS)
- Smart
- Fastly
- BunnyCDN
🎯 Simple summary:
- CDN = Global Web Accelerator
- By sending files from the point closest to the user.
- 🔥 Faster loading + More secure + Reduced load on main server
What is a web server and how does it work? ❓
Web Server It is a program or computer that provides data transfer services between a server and a client (or user) via the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) or HTTPS (HTTP Secure) protocol. A web server typically performs the following functions:
- Receive requests from browser (client) – When a user visits a website through a browser (e.g. Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari), the browser sends an HTTP request to the web server to request website data such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, or other files.
- Process requests and return data – The web server processes the requests received, such as searching for the requested files, or if a server-side script (e.g. PHP, Python, Ruby) is used, it processes data from the database and sends the results back to the browser.
- Reply information – After processing the request, the web server sends the appropriate information back to the user’s browser, such as the website window the user wants to access.
Examples of Web Server namely:
- Apache HTTP Server: One of the most widely used web servers.
- Nginx: A high-performance web server that is popularly used to support large volumes of traffic.
- Microsoft IIS (Internet Information Services): Web server developed by Microsoft.
Technically, a web server typically consists of:
- Hardware: A computer with web server software installed.
- Software: Software that manages the transmission of data and responds to user requests.
📘 Basic Web Hosting Terminology
| vocabulary | Easy-to-understand explanation |
|---|---|
| Web Hosting | A service for renting space to store website files on a server so that other people can access our website via the Internet. |
| Domain Name | Website name, such as example.com Used in place of the server's IP number. |
| Server | A computer that is always on, collecting and sending web data to users. |
| Shared Hosting | Hosting that allows multiple websites to share a server, cheap, suitable for beginners |
| VPS Hosting | Hosting that divides the server into multiple parts (like having a private server) is faster and more flexible than Shared Hosting. |
| Cloud Hosting | Hosting that uses multiple servers together makes the website stable and supports many users. |
| Dedicated Hosting | Renting a server for one person, high performance, suitable for large websites or organizations. |
| Bandwidth | The higher the amount of data sent from a website to users, the more users the website can support. |
| Data Transfer | The total amount of data transmitted through the website, such as downloading files or viewing images. |
| Disk Space | A place to store website files such as images, videos, and databases. |
| SSD | Faster storage than HDDs allows websites to load faster. |
| NVMe SSD | New SSDs are faster than regular SSDs, suitable for websites that require high speed. |
| Database | Website data storage, such as member lists, products, or orders. |
| cPanel | Control panel for managing hosting such as creating email, managing files, databases, etc. |
| FTP | How to send files from your computer to your website hosting |
| CMS | It is an abbreviation of Content Management System such as WordPress that helps to create a simple website. |
| WordPress | Popular CMS, easy to use, suitable for general websites, stores or blogs. |
| SSL Certificate | Security certificates give the site HTTPS and a padlock icon. |
| Uptime | The longer the website stays online, the closer to 100% the better (no website crashes). |
| CDN | A global network of servers helps websites load faster, especially from overseas. |
| Caching | Temporarily storing a copy of your website to make it load faster |
| DNS (Domain Name System) | A system that converts domain names into IP addresses to connect to real websites. |
📘 Web Hosting and Website Terminology (Additional)
| vocabulary | Easy-to-understand explanation |
|---|---|
| HTTP / HTTPS | Protocol used to communicate data between a website and its users; HTTPS is the more secure version. |
| IP Address | The server address, such as 123.45.67.89, is the actual address of the website. |
| Nameserver (NS) | The link between domain and hosting indicates which server the domain should load data from. |
| DNS Record | Various records in the DNS system such as A records, MX, CNAME that tell how a domain works. |
| A Record | DNS record that indicates which IP address a domain must go to. |
| CNAME | DNS records that point one domain to another domain to use data from. |
| MX Record | DNS records for managing email, such as telling which server emails should be sent to. |
| MySQL | Popular database systems used to store web data, such as WordPress, Joomla, etc. |
| PHP | Server-side scripting language used to create dynamic websites, such as WordPress using PHP. |
| Apache | Popular web server software used for server-side processing of websites. |
| Nginx | Another web server, faster and lighter than Apache in some cases. |
| Cron Job | The system will automatically schedule commands to run, such as ordering a backup every day at 2 a.m. |
| Backup | Backing up your website so you can recover it in case of a problem |
| Staging Site | A separate testing site from the main site, used for testing before the actual update. |
| TLD (Top-Level Domain) | The end of a domain name, such as .com, .net, .org, .co.th |
| Subdomain | A subdomain that is separate from the main domain, such as: blog.example.com |
| SFTP | Secure file transfer (more secure than FTP) |
| Firewall (WAF) | Website protection system against attacks such as blocking bots, SQL injection, DDoS |
| DDoS Attack | Attacking a website by sending a large amount of traffic to crash it. |
| cURL | A tool used to request data over HTTP, such as connecting to an API from another website. |
| API | A connection channel between systems, such as the web and database, or the web and other applications. |
| Latency | The latency time it takes for data to travel from the user to the server (the lower the better). |
| Load Balancer | The system distributes the load to multiple servers, preventing the website from crashing when there are a lot of customers visiting. |